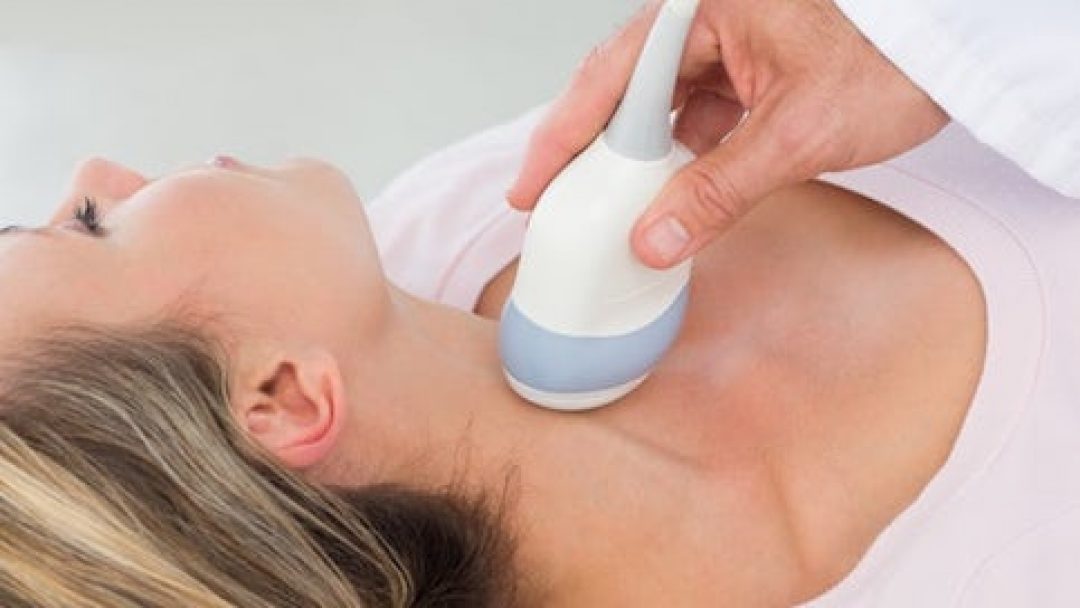
Researchers have recently said that a person’s risk of developing dementia can be predicted roughly 10 years before symptoms emerge with the help of a simple five-minute neck scan.
The scan works through analyzing the pulse of blood vessels within the neck.
Overall, dementia is an overarching term used to describe symptoms related to the loss of brain function. The World Health Organization claims that approximately 50 million people suffer from dementia worldwide, along with anticipating an increase to 152 million people by the year 2050.
According to the study by scientists at University College London (UCL), the scan has the potential to develop into routine testing for cognitive decline. On Sunday, the work was presented by UCL scientists at the American Heart Association’s annual scientific conference.
In 2002 alone, nearly 3,200 patients, ages 58-74, received neck ultrasounds prior to the monitoring of their cognitive functions over the next 14 years.
Leading to a greater and more irregular blood flow, those experiencing the most intense pulses were found to be up to 50% more probably to experience reduced cognitive functions. These findings were attributed to a damaged network of blood vessels within the brain that stemmed from the strength of which the blood traveled.
Poor diet, drug use and other lifestyle factors can lead to arteries close to the heart being worn down as a result of a rising intensity in pulses.
“If you can detect [the risk] in people in mid-life, it really gives an impetus to those people to change their lifestyle,” said Dr. Scott Chiesa, post-doctoral researcher at UCL. “What’s good for the arteries is good for the brain. Dementia is not an inevitable cause of aging. How you live your life has a real impact on how quickly your condition can decline.”
With the possibility of larger studies upholding the research findings down the road, there is a high increase the chances that dementia can be detected in middle age.
Thoughts of a future that involves early-detected dementia means scans would be “well set up for routine testing.” Chiesa also said “It’s very easy to do, and it’s very quick to do.”
Healthy arteries are found to help the heart regulate the blood being pumped away from the vital organ, which guarantees that there is a smooth and constant rate of flow to the brain.
On the flip side, damaged arteries lead to a more aggressive and irregular flow of blood through vessels leading into the brain. These changes can result in damage being done to the network of blood vessels and cells.
Researchers also believe that over an undisclosed period of time, there is an uptick in the frequency of cognitive decline within study participants.
“What we do know is that the blood supply in the brain is incredibly important, and that maintaining a healthy heart and blood pressure is associated with a lower risk of developing dementia,” said Carol Routledge, Director of Research at Alzheimer’s Research UK, who was not involved in the research.
Vascular dementia stems from a decrease in the blood flowing to the brain, which studies have found can have an influence on the development of Alzheimer’s disease. A large majority of dementia cases are found to originate from those vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s.
In the United States alone, dementia is the sixth biggest cause of death among adults, according to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. According to the Office for National Statistics, the disease has passed heart disease to become the leading cause of death in the United Kingdom.